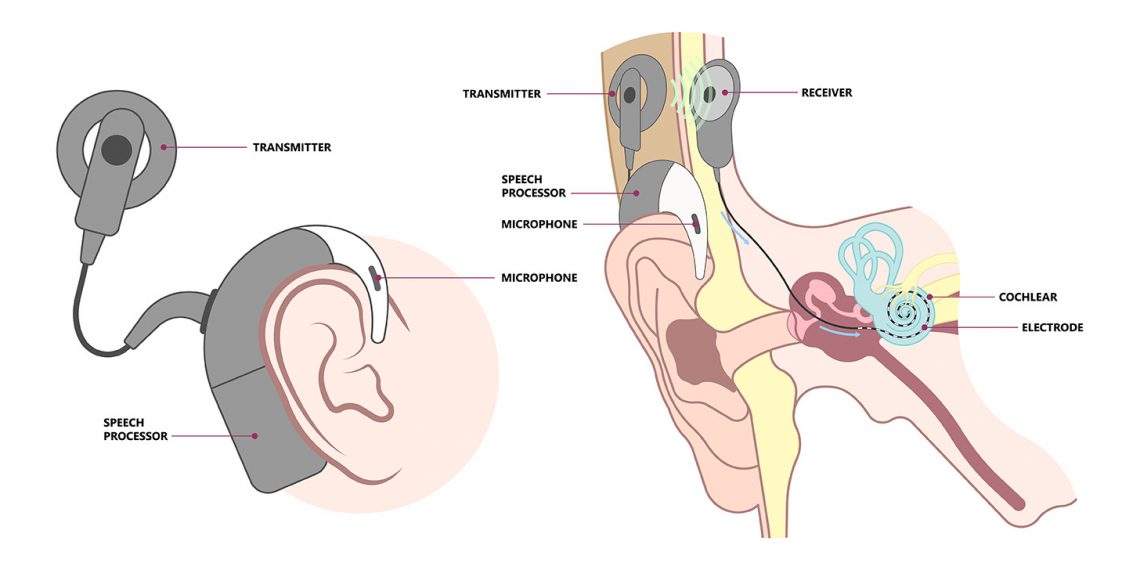
Conductive hearing loss is a type of hearing loss that occurs when sound is unable to reach the inner ear due to problems in the outer or middle ear. This type of hearing loss is different from sensorineural hearing loss, which occurs due to damage to the inner ear or the nerve pathways that transmit sound from the ear to the brain. The good news is that conductive hearing loss can often be treated, and the treatment depends on the underlying cause of the hearing loss.
One common cause of conductive hearing loss is earwax blockage. Earwax is a natural substance that helps to protect the ear from dust, bacteria, and other foreign particles. However, if too much earwax accumulates, it can block the ear canal and cause hearing problems. This type of conductive hearing loss can be easily treated with ear irrigation or ear wax removal, which involves using water or a special instrument to flush the earwax out of the ear canal.
Another common cause of conductive hearing loss is otitis media, which is an inflammation of the middle ear. Otitis media can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection, and it often occurs in children. Treatment options for otitis media include antibiotics, decongestants, or ear tubes. Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections, while decongestants can help to relieve swelling and improve the flow of fluid in the middle ear. Ear tubes are small plastic or metal tubes that are surgically placed in the eardrum to help drain fluid from the middle ear and improve hearing.
A perforated eardrum can also cause conductive hearing loss. A perforated eardrum is a tear or hole in the eardrum, which can be caused by an injury, infection, or other problem. Treatment for a perforated eardrum involves repairing the eardrum surgically. During this procedure, the surgeon will place a patch over the hole in the eardrum to restore its function and improve hearing.
Stapedius muscle paralysis is a rare condition that can cause conductive hearing loss. The stapedius muscle is responsible for moving the small bones in the middle ear, and if it is paralyzed, it can cause hearing problems. Treatment for stapedius muscle paralysis involves a surgical procedure called a stapedectomy. During this procedure, the surgeon will remove the damaged muscle and replace it with a small prosthesis to restore normal hearing.
Otosclerosis is a genetic condition that results in the abnormal growth of the bones in the middle ear. This can cause conductive hearing loss, as the bones in the middle ear are responsible for transmitting sound from the outer ear to the inner ear. Treatment options for otosclerosis include hearing aids or a surgical procedure called a stapedectomy. During a stapedectomy, the surgeon will remove the abnormal bone and replace it with a prosthesis to restore normal hearing.
Finally, some individuals are born with conductive hearing loss due to congenital anomalies of the ear structure. Treatment options for congenital conductive hearing loss may include surgery or the use of hearing aids. In some cases, a combination of medical and surgical interventions may be required to improve hearing.
Conductive hearing loss can often be treated with medical or surgical intervention, and the treatment depends on the underlying cause of the hearing loss. Regular hearing check-ups and prompt treatment of any ear problems can help maintain good hearing and prevent further hearing loss. If you are experiencing hearing problems, it’s important to consult a hearing specialist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
What Should I Do If I am Experiencing Conductive Hearing Loss Symptoms?
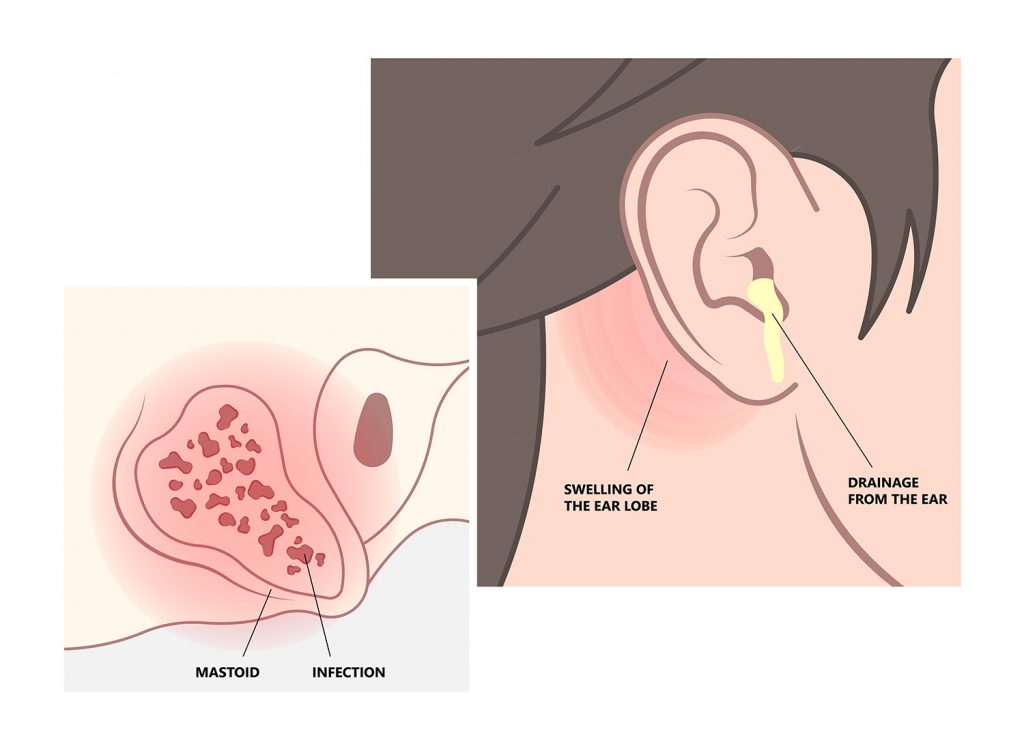
If you are experiencing symptoms of conductive hearing loss, it is important to take action as soon as possible to protect your hearing and improve your ability to hear and communicate. The first step is to schedule an appointment with an audiologist or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. They will be able to diagnose the cause of your hearing loss and recommend the best course of treatment for your specific needs.
During the appointment, the audiologist or ENT specialist will likely perform a physical examination of your ear and conduct a hearing test to determine the extent and cause of your hearing loss. They may also use other diagnostic tools, such as an ear drum light, to examine the inside of your ear and rule out any other underlying medical conditions.
Based on the results of the examination, your audiologist or ENT specialist may recommend a combination of treatments to help improve your hearing, including:
Medical treatment: If your conductive hearing loss is caused by a medical condition, such as an ear infection or a blockage in the ear canal, your audiologist or ENT specialist may prescribe medication or recommend surgery to treat the underlying condition.
Hearing aids: Hearing aids can be an effective solution for many individuals with conductive hearing loss. They work by amplifying sound and can help to overcome the effects of conductive hearing loss by providing a boost to the sound that reaches the inner ear. Your audiologist or ENT specialist can recommend the best type of hearing aid for your specific needs.
Assistive devices: If you have difficulty hearing in noisy environments or if you have trouble hearing the television or phone, your audiologist or ENT specialist may recommend assistive devices, such as amplifiers or telecoils, to help you hear more clearly.
Lifestyle changes: Making small changes to your lifestyle, such as avoiding noisy environments and wearing earplugs when necessary, can help to protect your hearing and prevent further hearing loss.
Speech therapy: If your conductive hearing loss is affecting your ability to communicate, speech therapy may be recommended to help you learn new strategies for communicating more effectively.
In addition to these treatments, it is also important to follow a healthy lifestyle to maintain good overall health and protect your hearing. This includes eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding activities that may put undue stress on your ears, such as excessively loud music or gunfire.
If you are experiencing symptoms of conductive hearing loss, it is important to take action as soon as possible to protect your hearing and improve your ability to hear and communicate. An audiologist or ENT specialist can help to diagnose the cause of your hearing loss and recommend the best course of treatment for your specific needs. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, you can overcome the effects of conductive hearing loss and enjoy improved hearing and communication.
How Can Hearing Aids Help With Conductive Hearing Loss?

Hearing aids can be an effective solution for individuals with conductive hearing loss. Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a problem in the outer or middle ear, preventing sound from reaching the inner ear. Hearing aids work by amplifying sound and can help to overcome the effects of conductive hearing loss by providing a boost to the sound that reaches the inner ear.
There are different types of hearing aids, including behind-the-ear (BTE) aids, in-the-ear (ITE) aids, in-the-canal (ITC) aids, and completely-in-the-canal (CIC) aids. The type of hearing aid that is best for a person with conductive hearing loss will depend on the severity of their hearing loss, their lifestyle, and their personal preferences.
Hearing aids work by amplifying sound and can be adjusted to suit an individual’s specific needs. They often have multiple programmable settings, which can be changed to suit different listening environments, such as quiet or noisy places. This helps to ensure that individuals with conductive hearing loss can hear clearly in a variety of situations.
One of the benefits of using hearing aids for conductive hearing loss is that they can provide relief from the frustration and social isolation that can accompany hearing difficulties. By improving an individual’s ability to hear and communicate, hearing aids can help to improve their quality of life and reduce the impact that conductive hearing loss has on their daily activities.
Another benefit of using hearing aids for conductive hearing loss is that they can be easily combined with other forms of treatment. For example, if an individual with conductive hearing loss has a perforated eardrum, they may need to have surgery to repair the eardrum. In this case, hearing aids can be used temporarily while the individual is recovering from surgery, and they can continue to use them even after the surgery to further improve their hearing.
Hearing aids also come with advanced features, such as directional microphones, which can help to improve an individual’s ability to hear in noisy environments. Some hearing aids also have the ability to connect to other devices, such as smartphones or televisions, allowing individuals with conductive hearing loss to enjoy their favorite activities without missing any important sounds.
Hearing aids can be an effective solution for individuals with conductive hearing loss. They work by amplifying sound, providing a boost to the sound that reaches the inner ear, and can help to improve an individual’s ability to hear and communicate. Hearing aids come in different types and sizes, and can be adjusted to suit an individual’s specific needs, making them a flexible and convenient solution for conductive hearing loss. With the right hearing aid, individuals with conductive hearing loss can enjoy improved hearing and reduced social isolation, improving their quality of life.