Sensorineural hearing loss is a type of hearing loss that occurs when there is damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or the nerve pathways that transmit sound from the inner ear to the brain. This type of hearing loss can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to hear and understand speech, especially in noisy environments.
Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis): This is the most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss and is associated with the natural aging process. As people age, their inner ear and auditory nerve can become less sensitive to sound, leading to a decline in hearing ability.
Exposure to loud noise: Prolonged exposure to loud noise, whether at work or during leisure activities, can damage the hair cells in the inner ear and cause sensorineural hearing loss. It is important to protect your hearing by wearing earplugs or other forms of hearing protection in noisy environments.
Ototoxic drugs: Certain medications, such as certain antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and some pain medications, can be toxic to the inner ear and cause sensorineural hearing loss. It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of any medications with your healthcare provider.
Infections: Viral and bacterial infections can cause damage to the inner ear and lead to sensorineural hearing loss. Some of the most common infections associated with sensorineural hearing loss include measles, mumps, meningitis, and rubella.
Trauma: Physical trauma to the head or ear can cause damage to the inner ear and lead to sensorineural hearing loss. This can include head injury, barotrauma (pressure-related injury caused by changes in air pressure, such as during air travel), or blast injury.
Genetics: Some forms of sensorineural hearing loss are hereditary and are caused by genetic mutations that are passed down from parent to child. This type of hearing loss can be present at birth or develop later in life.
Meniere’s disease: This is a rare disorder that affects the inner ear and can cause sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and vertigo (dizziness). The exact cause of Meniere’s disease is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an imbalance of fluid in the inner ear.
Chronic diseases: Certain chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and multiple sclerosis, can cause damage to the inner ear and lead to sensorineural hearing loss.
Tumors: Tumors, such as acoustic neuromas, can develop on the auditory nerve and cause sensorineural hearing loss. Treatment options for tumors will depend on the type, size, and location of the tumor, and may include surgery, radiation therapy, or observation.
Other medical conditions: Other medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders and neurological diseases, can cause damage to the inner ear and lead to sensorineural hearing loss.
It is important to note that sensorineural hearing loss can have multiple causes, and that a comprehensive evaluation by a licensed audiologist or hearing healthcare professional is necessary to determine the specific cause of hearing loss.
There are many causes of sensorineural hearing loss, including age-related hearing loss, exposure to loud noise, ototoxic drugs, infections, trauma, genetics, Meniere’s disease, chronic diseases, tumors, and other medical conditions. If you are experiencing hearing difficulties, it is important to seek the advice of a licensed audiologist or hearing healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment options.
What Should You Do If You Think You Have Sensorineural Hearing Loss?
If you think you are suffering from sensorineural hearing loss, it is important to seek a professional evaluation and treatment as soon as possible. Here are some steps you can take:
Schedule an appointment with an audiologist: An audiologist is a specialist trained in the evaluation and treatment of hearing loss. They will perform a thorough evaluation of your hearing, including a hearing test and medical history review, to determine if you have sensorineural hearing loss and the cause of your hearing loss.
Discuss your symptoms: During your appointment, be sure to discuss any symptoms you are experiencing, such as difficulty hearing in noisy environments, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), or dizziness. This information will help the audiologist determine the type and extent of your hearing loss.
Get a referral to a specialist if necessary: If the audiologist determines that you have a complex case of sensorineural hearing loss, they may refer you to a specialist, such as a neurologist or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) doctor, for further evaluation and treatment.
Consider hearing aids: If you are diagnosed with sensorineural hearing loss, your audiologist may recommend hearing aids as a treatment option. Hearing aids can help to amplify sounds and make it easier for you to hear and understand speech. Your audiologist will work with you to select the best hearing aids for your needs and budget.
Protect your hearing: To prevent further hearing loss, it is important to protect your hearing from exposure to loud noises. This can include wearing earplugs in noisy environments, limiting the use of headphones and earbuds, and avoiding exposure to loud concerts and fireworks.
Take care of your overall health: Maintaining good overall health can also help to prevent or slow the progression of sensorineural hearing loss. This includes eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing any chronic health conditions you may have.
Stay informed: Stay informed about the latest advancements in hearing loss treatment by talking to your audiologist and by reading reputable online sources. Advances in technology are making it possible for more people with sensorineural hearing loss to improve their hearing and live life to the fullest.
How Can Hearing Aids Help With Sensorineural Hearing Loss?
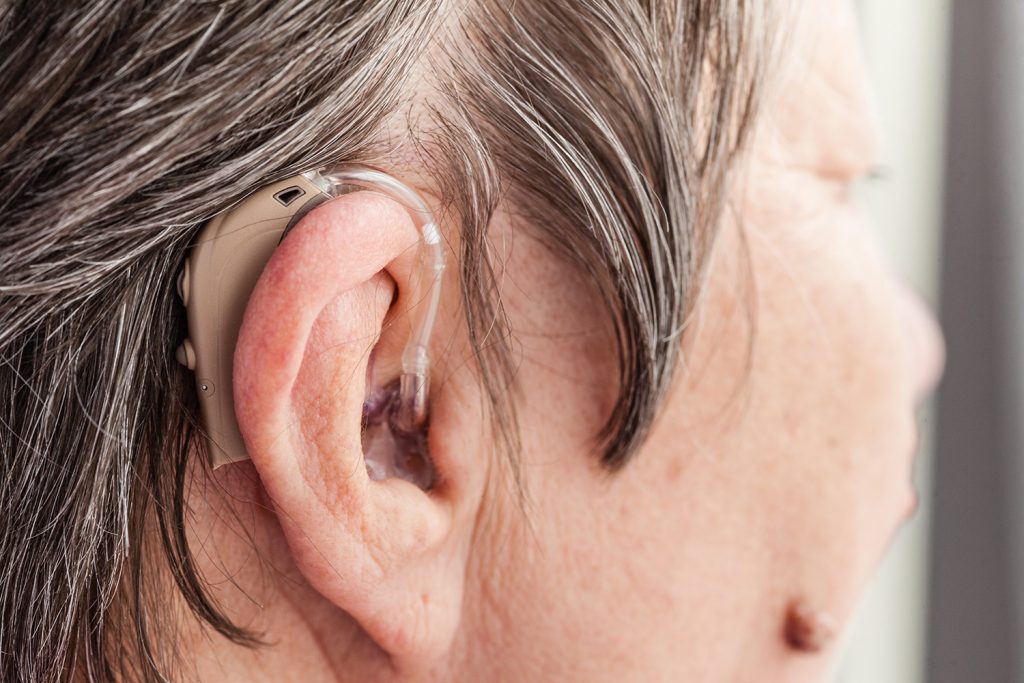
Hearing aids are one of the most common treatments for sensorineural hearing loss, a type of permanent hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve. Hearing aids work by amplifying sounds and making it easier for individuals with hearing loss to hear and understand speech. Here’s how they can help:
Improved speech understanding: Hearing aids amplify sounds, making it easier for people with hearing loss to understand speech, especially in noisy environments. This can help to improve communication with family and friends and increase social interaction.
Better overall hearing: Hearing aids can help to improve overall hearing by amplifying sounds and making it easier to hear faint or distant sounds. This can also help to reduce the strain on the listener and improve the ability to hear in noisy environments.
Customizable settings: Hearing aids can be customized to meet individual hearing needs. For example, they can be programmed to amplify specific frequencies to better match the listener’s specific hearing loss. This can help to improve the overall hearing experience and increase satisfaction with the hearing aid.
Improved quality of life: By improving hearing and communication, hearing aids can help to improve the quality of life for individuals with sensorineural hearing loss. This can lead to increased independence, better relationships, and increased participation in social and recreational activities.
Improved safety: By improving hearing, hearing aids can help to increase safety for individuals with hearing loss. For example, they can help individuals to hear warning signals and other important sounds, such as the doorbell or smoke alarm.
Wireless connectivity: Many modern hearing aids come equipped with wireless connectivity, which allows for improved sound quality and increased functionality. For example, some hearing aids can be connected to a smartphone or other device, allowing the user to control the hearing aid and adjust the volume and other settings from the device.
New technology: Advances in technology are constantly improving the hearing aid experience. For example, some new hearing aids are designed to be more comfortable, discreet, and easier to use, making them more appealing to individuals with hearing loss.
Hearing aids can be a highly effective treatment for individuals with sensorineural hearing loss. They work by amplifying sounds and making it easier for individuals to hear and understand speech, improving overall hearing, offering customizable settings, and providing a range of other benefits. With the right hearing aids and support, individuals with sensorineural hearing loss can regain the ability to hear and live life to the fullest.




